Air cylinders are a type of pneumatic actuator that convert compressed air energy into mechanical energy. The history of air cylinders can be traced back to the early 1900s, when pneumatic power started to become popular in industrial settings. The first pneumatic cylinders were simple devices that used compressed air to create linear motion. They were initially used in the mining industry to power drills and other equipment. Read More…
Bimba Manufacturing produces air cylinders, stainless steel air cylinders, rodless cylinders and a variety of other cylinders. We provide custom-designed air cylinders, quick delivery and a company-wide commitment to quality. Contact us for your cylinder needs today!
A world-class manufacturer of pneumatic, electro-mechanical & control components & systems, Festo has more than 75 years of experience in providing customer-driven automation solutions & service. Our vast selection of air cylinders includes a range of pneumatic cylinders that offer optimized performance for every application, with products meeting demands for the pharmaceutical industry.
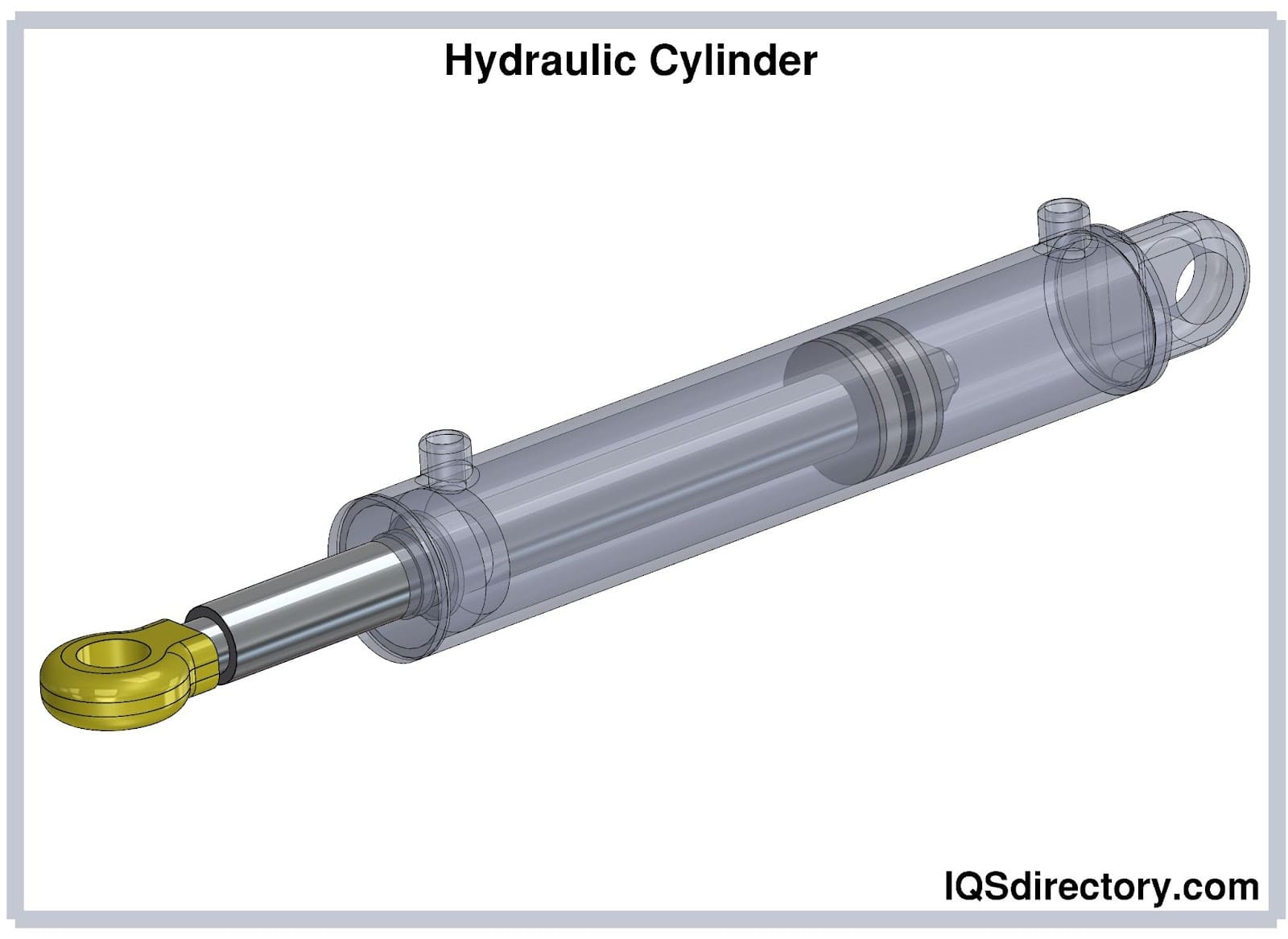
Falcon Industries is a machine shop and manufactures hydraulic and air cylinders to your exacting specifications. Our air cylinders are lightweight and durable. We specialize in repairable air cylinders for end dump trailers and belly (bottom) dump trucks, as well as pneumatic cylinders.

More Air Cylinders Manufacturers
What are Air Cylinders?
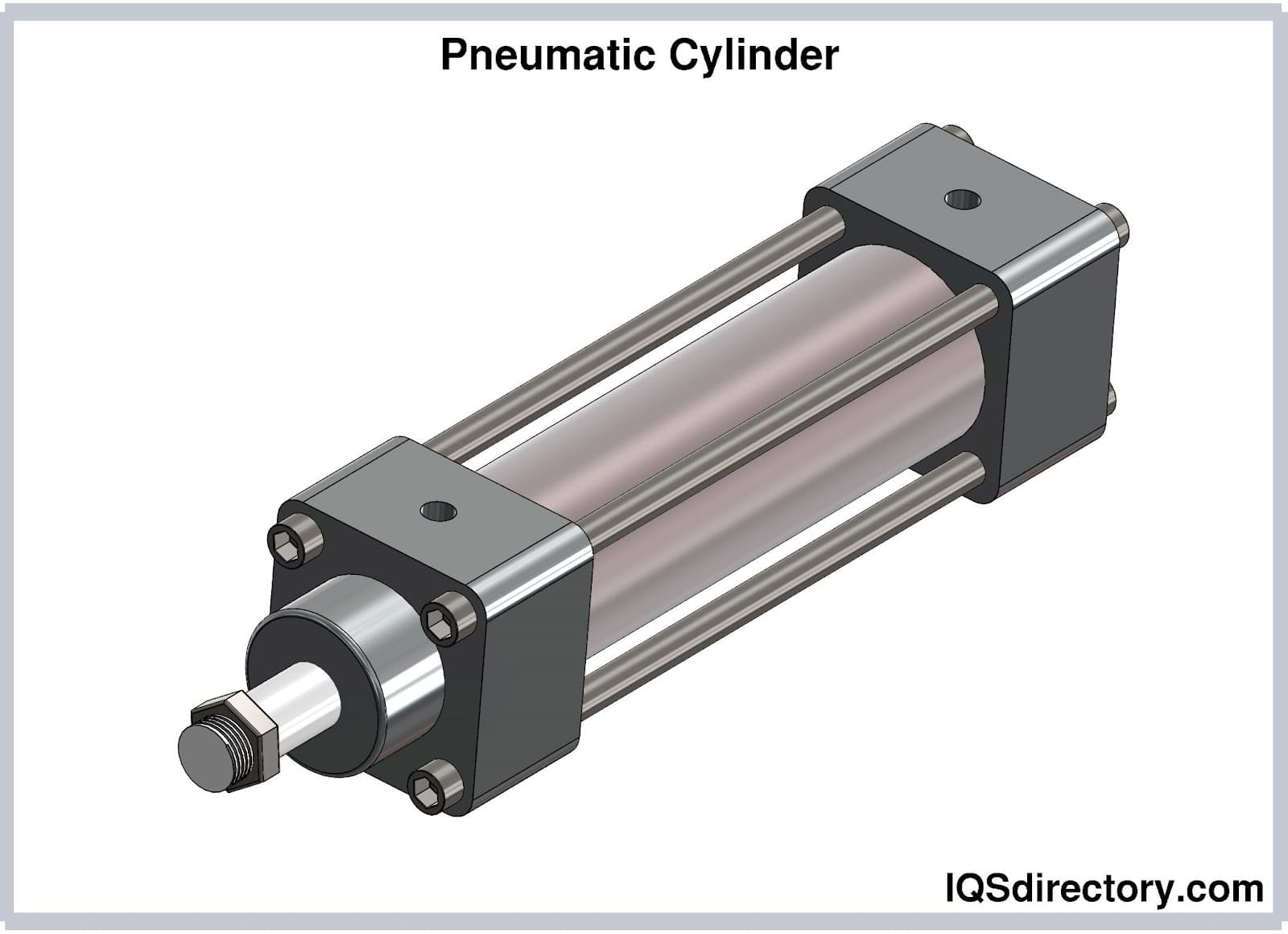
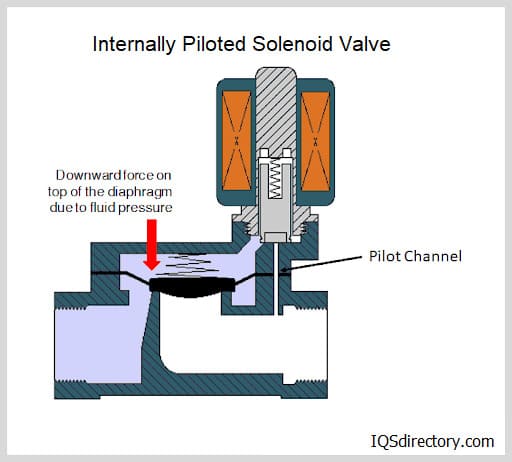
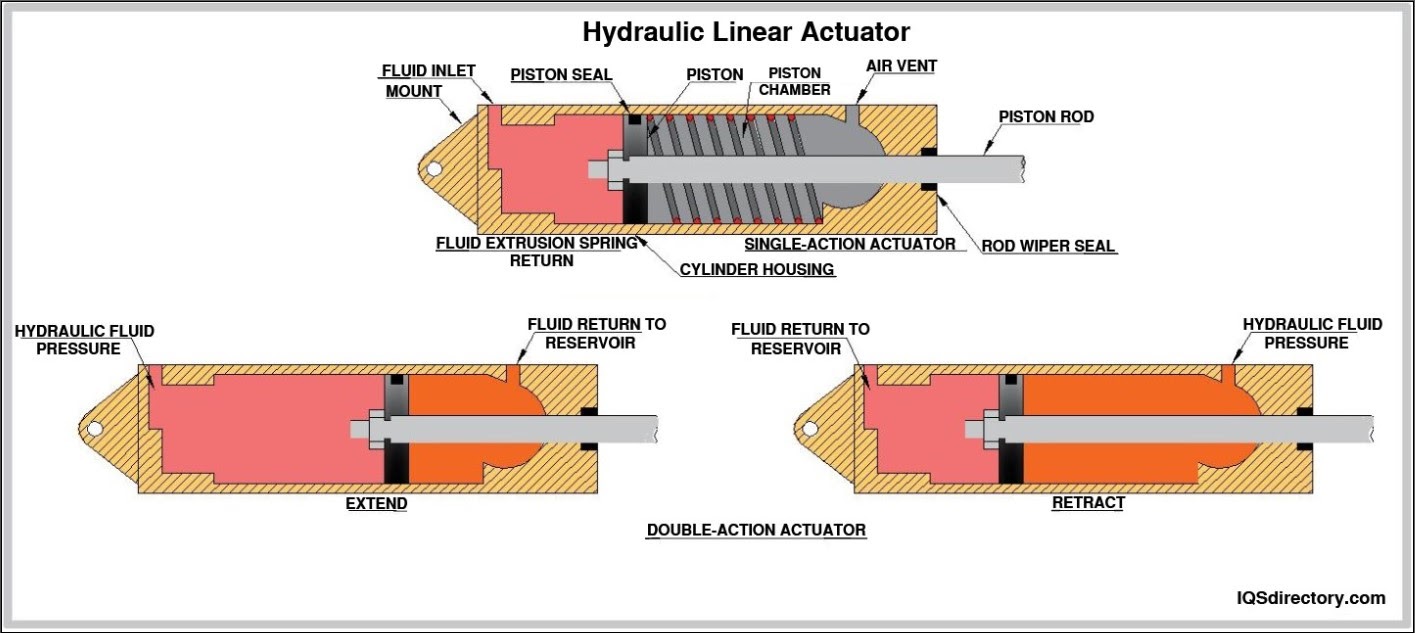
Answer: Air cylinders, commonly referred to as pneumatic cylinders, are essential actuators in modern automation and industrial systems. These mechanical devices transform compressed air energy into controlled linear motion, making them a core component in countless manufacturing, material handling, and process automation environments. Air cylinders are integrally composed of a cylindrical chamber, a piston, and a piston rod; when compressed air is introduced, it acts upon the piston to extend or retract the rod, creating force and movement to perform work such as lifting, pushing, pulling, or clamping.
Air cylinders are broadly divided into two fundamental categories: single-acting cylinders and double-acting cylinders. In single-acting types, compressed air drives the piston in one direction while a built-in spring or other external force returns it to its initial position. This configuration is ideal for applications requiring a simple, cost-effective push or pull action. In contrast, double-acting cylinders utilize air pressure on both sides of the piston, providing enhanced control and bidirectional force, making them suitable for more complex or heavy-duty automation tasks.
Manufactured from robust materials such as aluminum, steel, and stainless steel, pneumatic cylinders are selected based on their durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high internal and external pressures. The choice of material is often dictated by the operational environment—food processing, automotive assembly, and harsh outdoor locations all demand specific properties for optimal performance.
Air cylinders play a pivotal role in industrial automation systems, driving conveyor belts, robotic arms, and assembly lines. Their straightforward design, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a go-to solution for repetitive motion tasks in sectors ranging from electronics production to automotive manufacturing. In addition, their use extends to packaging machines, where they enable rapid sealing, cutting, and filling operations. The absence of electrical risk and the ability to deliver precise, adjustable force make air cylinders indispensable in industries prioritizing safety and consistent performance.
From their early adoption in manufacturing and transportation to their current applications in aerospace, robotics, medical devices, and smart factory systems, air cylinders have evolved to meet the demands of modern engineering. Advances in materials and control technology have only increased their efficiency, versatility, and integration within complex automated processes, cementing their status as a foundational component in global industry.

What are the Components of Air Cylinders?
Answer: Pneumatic cylinders are engineered from a range of specialized components, each contributing to the device’s ability to convert compressed air into reliable mechanical work. Understanding these parts helps buyers and engineers select the right air cylinder for their unique requirements, from heavy-duty manufacturing to precise laboratory automation. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the main components found in both standard and custom air cylinders:
- Cylinder Barrel (Body):
- The robust cylindrical housing encases the piston and maintains internal pressure. Typically crafted from aluminum for lightweight applications, steel for strength, or stainless steel for corrosion resistance, the barrel’s design directly impacts cylinder longevity and suitability for harsh or sanitary environments.
- Piston:
- The internal disc or cylindrical element that divides the barrel into two chambers. When compressed air is introduced, the piston moves, transmitting force to the piston rod. High-quality piston seals (often made from materials like nitrile or Viton) are crucial for preventing air leakage and ensuring efficient cylinder operation.
- Piston Rod:
- The linear shaft attached to the piston, extending outside the cylinder to deliver motion to external mechanisms. Typically constructed from hardened or chrome-plated steel, the piston rod’s surface treatment ensures durability, minimizes wear, and resists bending under load.
- End Caps (Head and Cap):
- The front (head) and rear (cap) covers seal the cylinder ends. The head end incorporates a rod hole fitted with seals and bushings, while the cap end closes the opposite side. Both ends feature air ports that enable controlled entry and exit of compressed air.
- Seals:
- Critical for maintaining pressure, seals (such as O-rings, U-cups, or lip seals) are found around the piston and rod. Advanced elastomer materials ensure leak-free operation and tolerate temperature and chemical exposure, essential for high-cycle industrial applications.
- Ports:
- Openings on the end caps allow compressed air to flow in and out of the cylinder. Double-acting cylinders have ports on both ends, enabling bidirectional control, while single-acting types typically have a single port and a spring return mechanism.
- Cushions (Optional):
- Adjustable air or polymer pads integrated at the cylinder ends. Cushions decelerate the piston at the end of its stroke, reducing impact, noise, and wear—crucial for high-speed or heavy-load automation processes.
- Mounting Hardware:
- Includes brackets, flanges, clevises, and trunnions, enabling secure installation of the air cylinder on machinery or structural frames. The choice of mounting style (such as foot mount, flange mount, or trunnion mount) influences alignment, stability, and ease of replacement.
- Spring (Single-Acting Cylinders Only):
- A coil spring returns the piston to its resting position when air pressure is released, allowing for a simplified return mechanism in basic push or pull applications.
- Bearings/Bushings:
- Located in the head end, bearings and bushings support and guide the piston rod, minimizing friction and wear while ensuring smooth, accurate motion over millions of cycles.
The precise design, configuration, and materials of these components are determined by the cylinder’s intended use—whether it’s for high-speed packaging, heavy industrial lifting, or delicate positioning in medical equipment. By understanding how these components interact, engineers and maintenance professionals can better troubleshoot, maintain, and specify cylinders that deliver consistent performance and value.
Types of Air Cylinders
When researching pneumatic actuators, it’s important to recognize the broad array of air cylinder types available, each engineered to address different application needs, space constraints, and operational requirements. Here’s an overview of the most prevalent types, along with guidance to help you compare features and select the optimal solution:
- Single-Acting Cylinders: Employ air pressure to move the piston in one direction, with a spring or external force providing the return stroke. These are valued for their simplicity and are ideal for applications requiring straightforward movement, such as ejecting parts from a mold or opening a valve.
- Double-Acting Cylinders: Utilize air on both sides of the piston for full bidirectional control. This configuration supports more complex automation tasks, precise positioning, and higher force output in both extension and retraction—making them a staple in industrial robotics, automotive assembly, and material handling systems.
- Rodless Cylinders: Feature a moving carriage or magnetic coupling inside the barrel instead of a protruding piston rod, enabling long strokes within a compact footprint. Rodless cylinders excel in applications where space is limited or where the risk of rod bending must be minimized, such as in printing presses or large-format packaging equipment.
- Rotary Actuators: Convert air pressure into rotational (rather than linear) motion, enabling precise turning, indexing, or valve actuation. These are popular in automated machinery that requires controlled rotation or angular positioning.
- Compact Cylinders: Designed for minimal envelope size without sacrificing performance, these cylinders are often used in tight spaces or lightweight assemblies. Their short overall length makes them ideal for medical devices, electronics assembly, and portable tools.
- Tandem and Multi-Position Cylinders: Combine multiple pistons or stages to achieve higher forces or allow for multiple stopping positions within a single actuator, enhancing flexibility in custom automation setups.
- Guided Cylinders: Feature integrated guide rods or bearings alongside the piston rod for superior stability and anti-rotation control, essential for precise linear guidance in pick-and-place or pressing operations.
By understanding these configurations, you can match cylinder selection to your application—whether you prioritize force, precision, space efficiency, or motion type (linear vs. rotary). Need help identifying the best cylinder for your use case? Ask: What type of air cylinder is best for my automation or production environment?

Limitations of Air Cylinders
While air cylinders offer numerous benefits for industrial automation and motion control, it’s vital to understand their operational limitations to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are several key drawbacks to consider when specifying pneumatic cylinders for your system:
- Contamination Sensitivity: Dust, dirt, and airborne particles can infiltrate the cylinder or air supply, damaging seals and internal surfaces. This can lead to air leakage, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance frequency. Implementing proper filtration and regular preventive maintenance is essential.
- Temperature Constraints: Extreme heat or cold can degrade seals, alter material properties, and impair lubricant performance. High temperatures may cause seal swelling or breakdown, while low temperatures can stiffen elastomers and slow piston movement.
- Limited Speed and Force Control: Although air cylinders are fast-acting, they can be challenging to finely control in terms of speed and positioning compared to electric or hydraulic actuators. Variations in air supply pressure and flow can result in inconsistent performance for high-precision applications.
- Air Supply Dependency: Pneumatic actuators require a stable source of compressed air. Fluctuations in pressure or quality can reduce force output and operational reliability, especially in facilities with extensive or aging air distribution systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Compressed air systems can be less energy-efficient than electric actuation, especially if there are system leaks or inefficient compressors. This can increase operational costs over time.
Curious how to overcome common air cylinder challenges? Explore preventative maintenance strategies or ask: What best practices improve pneumatic cylinder longevity and performance?
Benefits of Air Cylinders
Despite their limitations, air cylinders remain a preferred choice in countless industries due to their unique advantages. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits driving their widespread adoption:
- Low Maintenance Requirements: With fewer moving parts and no need for complex lubrication systems, pneumatic cylinders often require only routine inspection and seal replacement, resulting in lower total cost of ownership over their lifecycle.
- High Force Output Relative to Size: Air cylinders can generate substantial force with compact physical dimensions, making them ideal for heavy-duty pressing, clamping, or lifting in confined spaces.
- Quick Response and High Cycling Rates: Their inherent design enables rapid acceleration and deceleration, supporting high-speed operations in packaging, sorting, or assembly lines.
- Simple, Robust Construction: The straightforward design makes air cylinders reliable, easy to install, and less susceptible to catastrophic failure than complex electro-mechanical systems.
- Safety in Hazardous Environments: Because they do not generate sparks or rely on electrical power, pneumatic cylinders are inherently safer in explosive, wet, or corrosive environments—ideal for mining, chemical processing, or food manufacturing.
- Scalability and Customization: Manufacturers offer a wide range of standard and custom cylinders, enabling tailored solutions for unique stroke lengths, mounting configurations, and environmental needs.
Want to compare pneumatic actuators to electric or hydraulic options? Ask: What are the advantages of air cylinders over other actuation technologies?
What are the Applications of Air Cylinders?
Answer: Air cylinders are a cornerstone of industrial motion control, delivering reliable, efficient, and safe actuation across a vast array of industries and applications. Here’s how pneumatic cylinders are used to power productivity and innovation:
Industrial Automation
- Assembly Lines: Drive robotic arms, pick-and-place units, and grippers for repetitive tasks such as part insertion, alignment, or packaging. Pneumatic cylinders enhance throughput, precision, and consistency.
- Material Handling: Operate lifters, pushers, and sorting devices to move products efficiently between production stages, reducing manual labor and streamlining workflow.
- Automated Testing: Apply force for quality assurance, pressing, or measuring components to verify product specifications.
Manufacturing
- Presses and Stamping: Power presses for metal forming, embossing, or cutting, where consistent force is essential for quality control in automotive, appliance, and electronics manufacturing.
- Tooling and Fixturing: Clamp, index, or hold workpieces securely during machining, welding, or assembly processes, ensuring repeatable accuracy and operator safety.
Automotive Industry
- Production Lines: Lift and position body panels, doors, or chassis components, and actuate brakes or suspension systems during assembly and end-of-line testing.
- Service Equipment: Drive pneumatic jacks, vehicle lifts, and tire changers, leveraging the high force and adjustability of air cylinders for heavy vehicle maintenance.
Packaging and Processing
- Sealing and Cutting: Enable high-speed heat-sealing, trimming, and slicing of packaging materials, supporting rapid throughput in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical lines.
- Filling Systems: Precisely position bottles, cans, or cartons and actuate dispensing valves for accurate, repeatable filling operations.
Construction and Agriculture
- Heavy Equipment: Extend and retract arms, buckets, or blades in excavators, loaders, and tractors, performing repetitive motion tasks under harsh outdoor conditions.
- Irrigation and Fluid Control: Automate valve actuation in water management or chemical spraying systems, improving efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
Aerospace and Defense
- Component Testing: Simulate real-world movements of landing gear, control surfaces, or actuators in flight simulators and test benches.
- Precision Assembly: Position structural and electronic components during aircraft and spacecraft manufacturing, where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Medical and Laboratory Automation
- Equipment Actuation: Adjust patient beds, dental chairs, or surgical tables, offering smooth, quiet, and spark-free operation in sensitive healthcare environments.
- Lab Automation: Drive pipetting robots, sample handlers, or analytical devices where contamination-free, controlled motion is required.
- Prosthetics: Integrate lightweight pneumatic actuators into advanced artificial limbs for enhanced strength and mobility.
Energy Sector
- Wind and Solar: Use air cylinders to adjust turbine blades or solar panel orientation, maximizing efficiency and longevity in renewable energy installations.
- Oil and Gas: Automate valve actuation and pipeline controls in high-pressure, hazardous environments where electrical actuation may be impractical or unsafe.
HVAC and Building Automation
- Climate Control: Modulate air dampers, valves, or louvers in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for energy-efficient building management.
Advantages Driving Applications
Air cylinders excel where rapid, repeatable motion is needed without electrical hazards, such as in explosive or wet environments. Their adjustable force, simplicity, and compatibility with plant-wide automation systems make them a flexible, scalable choice for everything from delicate electronics assembly to heavy industrial lifting and material transport.
Looking for application-specific guidance? Ask: Which air cylinder type is best for packaging, automotive assembly, or laboratory automation?

The Future of Air Cylinders
As industrial automation, robotics, and smart manufacturing continue to advance, the future of air cylinders looks dynamic and promising. Ongoing innovations in materials science, manufacturing methods, and digital integration are setting the stage for next-generation pneumatic actuators that deliver even greater efficiency, reliability, and intelligence.
Key trends shaping the future of pneumatic cylinders include:
- Advanced Sealing Technologies: Research into friction-reducing, self-lubricating, and wear-resistant seals is expected to further minimize leaks and maintenance needs, boosting uptime and lowering operational costs.
- Lighter and More Compact Designs: The adoption of advanced alloys and composites will allow manufacturers to offer smaller, lighter cylinders without sacrificing strength or durability, ideal for applications where space and weight are at a premium.
- Smart Pneumatics: Integrated sensors, IoT connectivity, and real-time diagnostics will enable predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and dynamic control—ushering in the era of Industry 4.0. Smart air cylinders will provide valuable data on position, cycle count, and health status, helping operators maximize productivity and reduce unscheduled downtime.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Enhanced valve designs, leak detection systems, and air management technologies will improve the energy profile of pneumatic systems, making them more sustainable and cost-effective for large-scale operations.
- Expanded Application Scope: With increasing precision and adaptability, future air cylinders will play a vital role in emerging sectors such as collaborative robotics (cobots), medical diagnostics, and renewable energy systems.
Wondering how smart cylinders can benefit your facility? Ask: What features should I look for in next-generation pneumatic actuators for Industry 4.0?
The evolution of air cylinders is unlocking new opportunities across diverse fields—from advanced robotics and healthcare to energy management and beyond. As demands for precision, speed, and sustainability grow, pneumatic cylinders will continue to adapt and deliver reliable mechanical motion wherever it’s needed.
Choosing the Right Air Cylinder Manufacturer
Selecting the optimal air cylinder for your application begins with choosing a reputable, knowledgeable manufacturer. The right supplier can provide expert guidance, ensure high-quality standards, and offer custom solutions to meet your unique operational needs. Here’s how our directory can help streamline your search and procurement process:
- Comprehensive Manufacturer Listings: Access detailed business profiles featuring each manufacturer’s product range, industry experience, and core competencies—allowing you to compare capabilities at a glance.
- Direct Contact and RFQ Tools: Use integrated contact forms to request information, quotes, or technical support directly from multiple suppliers, saving time and ensuring competitive pricing.
- Website Previewer: Explore each company’s specialization and digital presence quickly before making contact, helping you shortlist the best-fit vendors for your application.
- Expert Consultation: Many manufacturers offer engineering support to help you specify cylinder dimensions, mounting styles, materials, and options tailored to your environment and requirements.
- Custom Solutions: If your application demands non-standard stroke lengths, high-temperature seals, or unique mounting hardware, leading manufacturers can design and produce custom pneumatic cylinders to your exact specifications.
Ready to compare leading air cylinder suppliers? Start by visiting our manufacturer directory or use our RFQ form to reach out to multiple vendors with your project details.
By leveraging our resources and connecting with trusted experts, you can confidently evaluate, source, and implement air cylinders that deliver lasting value, performance, and safety in any industrial, commercial, or research application.
—
Frequently Asked Questions about Air Cylinders
- How do I choose the right type of air cylinder for my application?
Consider factors like required force, stroke length, mounting space, motion type (linear vs. rotary), and operating environment. Consulting with a manufacturer or automation specialist can help match your needs with the optimal product. - What maintenance is required for pneumatic cylinders?
Regular inspection of seals, lubrication (if specified), and air supply filtration are key to maintaining peak performance. Replace worn seals promptly and keep the air supply clean and dry for best results. - Can air cylinders be used in hazardous or cleanroom environments?
Yes—select models feature corrosion-resistant materials, food-grade seals, and spark-free operation, making them suitable for use in food processing, pharmaceuticals, or explosive atmospheres. - What are common signs that an air cylinder needs repair or replacement?
Look for air leaks, slow or inconsistent motion, sticking pistons, or visible damage to rods and seals. Prompt attention can prevent costly downtime or equipment damage.
—
Explore More Resources
- Learn about double-acting cylinder applications
- Discover compact pneumatic solutions for tight spaces


 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services