At American Cylinder Co., Inc., we manufacture high-quality air cylinders designed to meet the performance demands of a wide range of industrial applications. Our team specializes in crafting both standard and custom pneumatic cylinders with precision and durability in mind.
Pneumatic Cylinders & Couplers is a manufacturer of NFPA tie rod aluminum and stainless steel cylinders, pneumatic cylinders as well as special designs to meet unique customer applications. Pneumatic Cylinders & Couplers products are used in the food processing, printing and packaging industries. Visit our website today to view our online catalogs for more information!
PHD, Inc., is a leading, ISO 9001 certified manufacturer of industrial automation actuators designed to help companies optimize their manufacturing processes. Our products consist of a full line of cylinders, escapements, grippers, linear slides, rotary actuators, clamps, multi-motion actuators, switches and sensors.

More Compressed Air Cylinder Manufacturers
Compressed air cylinders, also known as pneumatic cylinders or air actuators, are critical components in modern automation and industrial systems. These versatile devices harness the power of compressed air to generate linear or rotary motion, enabling efficient movement and control of machinery. Whether you’re exploring ways to enhance manufacturing productivity, improve equipment reliability, or optimize motion control systems, understanding the roles and applications of compressed air cylinders is essential. What are the advantages of pneumatic actuators in your industry? Read on to discover key insights, applications, and decision factors that will help you choose the right solution for your needs.
Air cylinders serve as integral parts of a wide range of machinery and industrial processes. For example, they are fundamental in air brake systems for large trucks, serve as actuators in packaging lines, and are pivotal in factory automation where precise, repeatable motion is required. Their ability to open and close heavy doors, automate repetitive tasks, and provide reliable linear force makes them indispensable across industries. Is it any wonder that these robust pneumatic solutions are vital to most businesses and sectors seeking efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness?
Industries That Rely on Compressed Air Cylinders
Compressed air cylinders are the backbone of many industrial and commercial applications, providing the mechanical force necessary for automation, handling, and processing. The following industries particularly benefit from the use of air cylinders and their various specialized configurations:
- Automotive production – Used in assembly lines for welding, painting, material handling, and automated tool changers.
- Supply chain logistics – Vital in sorting, packaging, and conveying systems to move goods efficiently.
- Food and beverage processing – Enable hygienic, reliable actuation in product handling, sorting, and packaging machinery.
- Electronics manufacturing – Precise actuation for pick-and-place robots, PCB assembly, and delicate component handling.
- Mining and material handling – Heavy-duty pneumatic cylinders operate in harsh environments for ore transport and equipment control.
- Packaging and bottling – Facilitate fast, repeatable motion in filling, sealing, labeling, and palletizing operations.
- Pharmaceutical production – Ensure clean, reliable, and contamination-free motion in automated systems.
- Textile and printing – Used for fabric tensioning, cutting, and automated press operations.
How Compressed Air Cylinders Work: The Science Behind Pneumatic Motion
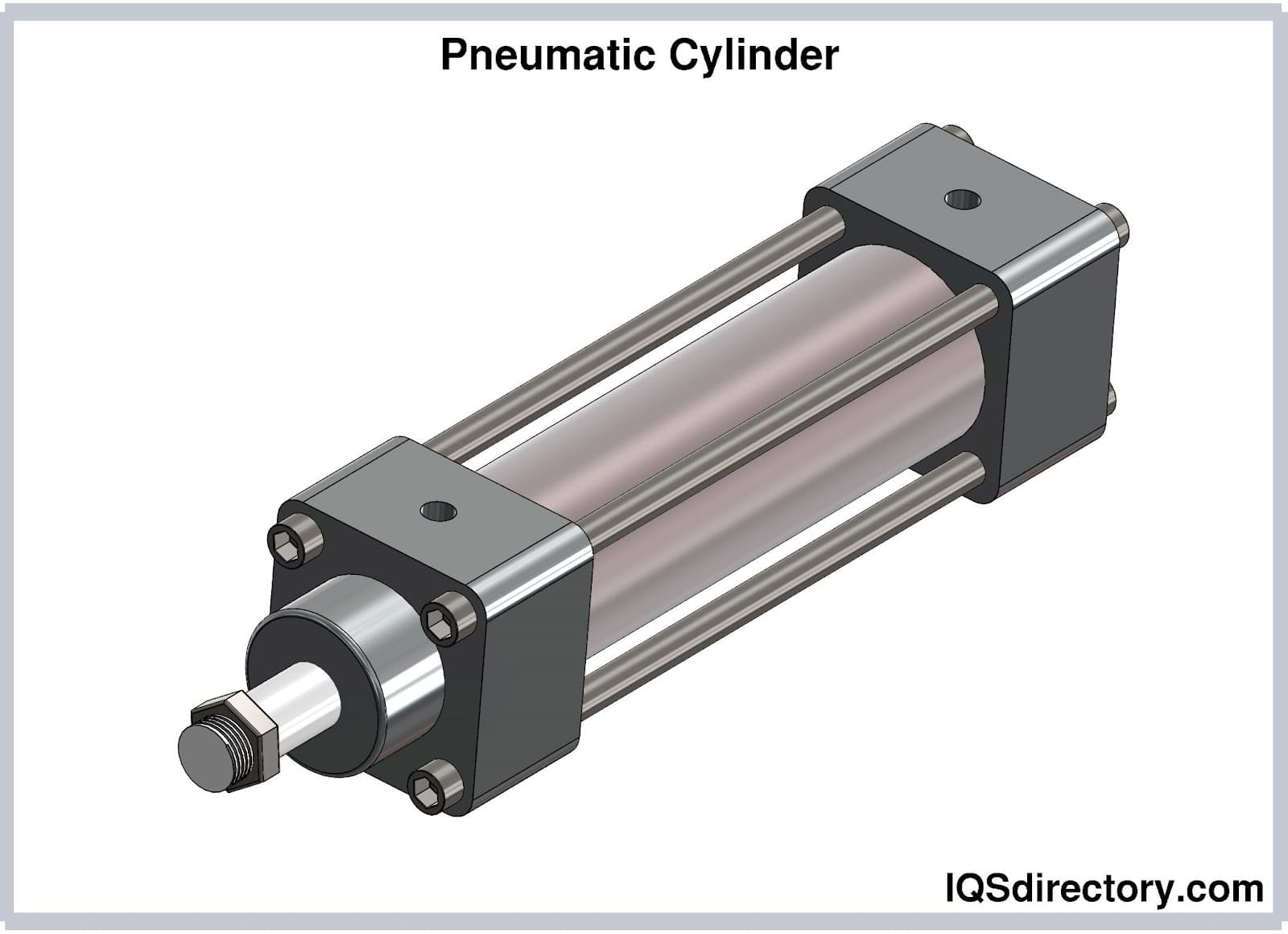
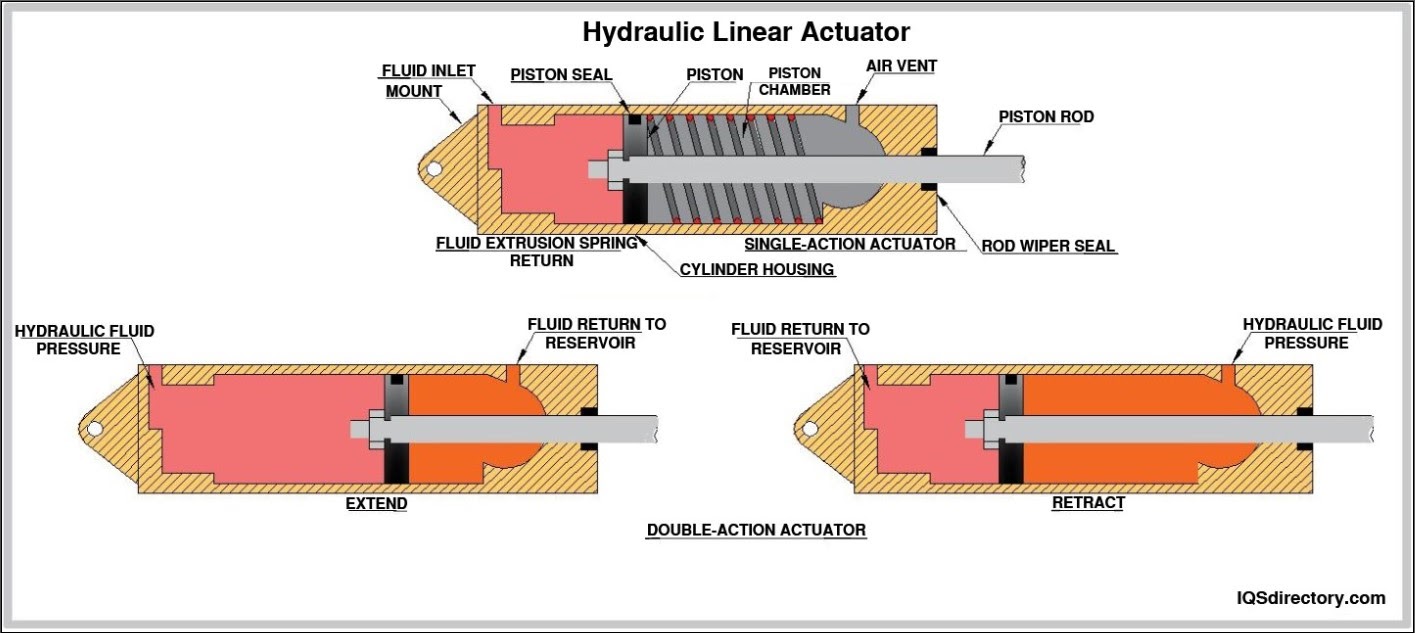
Compressed air cylinders convert the potential energy stored in compressed gases into precise, controlled mechanical energy. The core components of an air cylinder include:
- Cylinder barrel – Houses the piston and maintains the pressure differential.
- Piston and piston rod – Moves within the cylinder, transferring force to external mechanisms.
- End caps and seals – Ensure airtight operation and direct airflow to specific chamber sides.
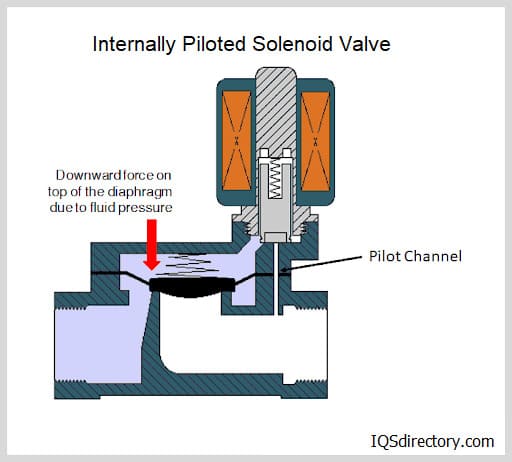
- Inlets/ports – Allow compressed air to enter or exit the cylinder, controlled by solenoid or pneumatic valves.
When compressed air is introduced into one side of the cylinder, the piston moves, creating linear or rotary motion. The direction, speed, and force of this motion are managed through precise air pressure regulation and valve timing. Cylinders can be configured in various sizes and mounting styles, depending on the application’s load requirements and space constraints. Want to know which pneumatic actuator fits your project? Explore different air cylinder types for your specific needs.

Common Types of Compressed Air Cylinders
Choosing the right type of air cylinder depends on your application’s force, speed, and space requirements. The most popular pneumatic actuator types include:
- Single-acting cylinders
- Double-acting cylinders
- Rodless cylinders
- Rotary actuators
- Tandem and multi-position cylinders
- Compact and mini cylinders
- ISO and NFPA standard cylinders
Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders

Single-acting cylinders operate in one direction only. Compressed air pushes the piston in one direction, while a built-in spring returns it to its original position when the air is exhausted. These actuators are lightweight, economical, and ideal for applications where the return stroke does not require force, such as:
- Clamping and holding operations
- Lightweight industrial automation
- Door opening/closing mechanisms
- Simple ejector or punch devices
Because they consume air only during one half of the cycle, single-acting cylinders are energy-efficient and cost-effective for repetitive, low-force tasks.
Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders

Double-acting cylinders, the most widely used in industrial automation, utilize compressed air to move the piston in both directions. This design allows for full control of extension and retraction, providing consistent force throughout the entire stroke. Applications include:
- Pick-and-place automation
- Robotic end-effectors
- Material transfer systems
- Automated assembly lines
- Packaging and labeling equipment
Double-acting cylinders are available in a wide array of bore sizes, stroke lengths, and mounting options, making them suitable for tasks requiring higher force, precise positioning, or continuous operation. Learn more about double-acting cylinders and their industrial benefits.
Rodless and Compact Cylinders
Rodless air cylinders eliminate the external piston rod, allowing for longer strokes in a compact footprint. These cylinders are ideal for applications where space is limited, such as sliding doors, conveyor positioning, and linear transport in packaging or electronics assembly. Compact and miniature cylinders, with diameters as small as 2.5 mm, provide precise actuation for delicate or space-constrained operations.
Rotary Pneumatic Cylinders
Rotary actuators convert compressed air into rotational motion, commonly used for indexing, sorting, or turning mechanisms in manufacturing and process automation. These cylinders can be configured for specific angles or continuous rotation, offering versatile solutions for automated assembly and handling.
How to Size and Select the Right Air Cylinder
Selecting the optimal compressed air cylinder for your application involves careful consideration of several key parameters:
- Bore size: Determines the force output – larger bores deliver higher force at the same pressure.
- Stroke length: The distance the rod or load must travel.
- Operating pressure: Typical pneumatic systems run at 60-120 psi, but requirements may vary.
- Mounting configuration: Includes front/rear flange, foot, clevis, trunnion, and more; affects alignment and load support.
- Cushioning and speed control: Internal cushions or adjustable flow controls help manage impact and speed at the end of travel.
- Environmental factors: Temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals, and cleanliness requirements.
- Cycle frequency and expected life: Higher cycle rates or demanding duty cycles require robust, durable cylinder construction.
- Feedback and position sensing: Magnetic or electronic sensors for process control and automation feedback.
Need help with cylinder sizing or pneumatic actuator selection? Request a quote or expert consultation to ensure the best fit for your system.
Key Benefits of Using Compressed Air Cylinders
Why are compressed air cylinders favored in so many automation and industrial applications? Their unique benefits make them a leading choice for reliable, efficient actuation:
- Lightweight energy source: Pneumatic systems are lighter than hydraulics and easier to install in mobile or overhead applications.
- High adaptability: Usable across diverse sectors, from cleanrooms to heavy manufacturing, due to the wide range of available materials and sealing options.
- Directional flexibility: Capable of providing linear or rotary motion in multiple directions and axes.
- Versatile mounting options: Wide selection of mounting brackets and hardware for varied installations.
- Customizable configurations: Standard and custom designs, including tandem, multi-position, and guided cylinders for complex needs.
- Cost-effective and sustainable: Compressed air is readily available, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly compared to hydraulic fluids.
- Feedback integration: Sensors and switches can be added for advanced automation and process monitoring.
- Safe operation: No risk of fluid leaks or contamination, making them suitable for food, pharmaceutical, and cleanroom environments.
- Fast and consistent cycling: Ideal for high-speed automation with reliable repeatability and low maintenance requirements.

Pneumatic Cylinder Applications: Real-World Use Cases
Compressed air cylinders play a pivotal role in countless industrial and commercial applications. Here’s how they’re commonly used:
- Automated manufacturing: Transfer arms, clamping fixtures, and pressing tools utilize pneumatic cylinders for fast, repeatable movement.
- Robotics: End-of-arm tooling, grippers, and actuators in collaborative robots (cobots) rely on precise air control.
- Material handling: Conveyor diverters, lifters, and indexing tables benefit from robust air-powered actuation.
- Vehicle systems: Air brake systems, suspension controls, and door openers in buses, trucks, and trains.
- Packaging lines: Filling, capping, labeling, and palletizing equipment use pneumatic cylinders for speed and hygiene.
- Medical devices: Non-lubricated, cleanroom-compatible cylinders deliver precise actuation for laboratory and pharmaceutical automation.
- Construction machinery: Pneumatic hammers, jackhammers, and drilling rigs utilize heavy-duty air cylinders for reliable force delivery.
- Entertainment and stage automation: Moving props, platforms, and effects with quiet, precise pneumatic actuation.
Curious about specific industry solutions? Explore in-depth use cases to see how pneumatic cylinders can solve your unique automation challenges.
Limitations and Considerations: Drawbacks of Compressed Air Cylinders
While pneumatic cylinders offer numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of their limitations to ensure optimal system design:
- Variable force output: Single-acting compact cylinders may not deliver constant force across the full piston stroke due to spring return mechanisms, limiting their effectiveness in some applications.
- Safety concerns: Unexpected release of compressed air or mechanical failure (such as a damaged valve cap) can pose safety hazards. Proper installation, regular inspections, and safety guards are essential.
- Compressibility of air: Unlike hydraulic fluids, air is compressible, which can result in less precise control of speed and position, especially under varying loads.
- Friction losses: At low speeds, frictional forces in seals and guides may reduce efficiency and smoothness of motion.
- Energy efficiency: Some pneumatic systems may waste energy through leaks or excessive air consumption if not properly maintained or sized.
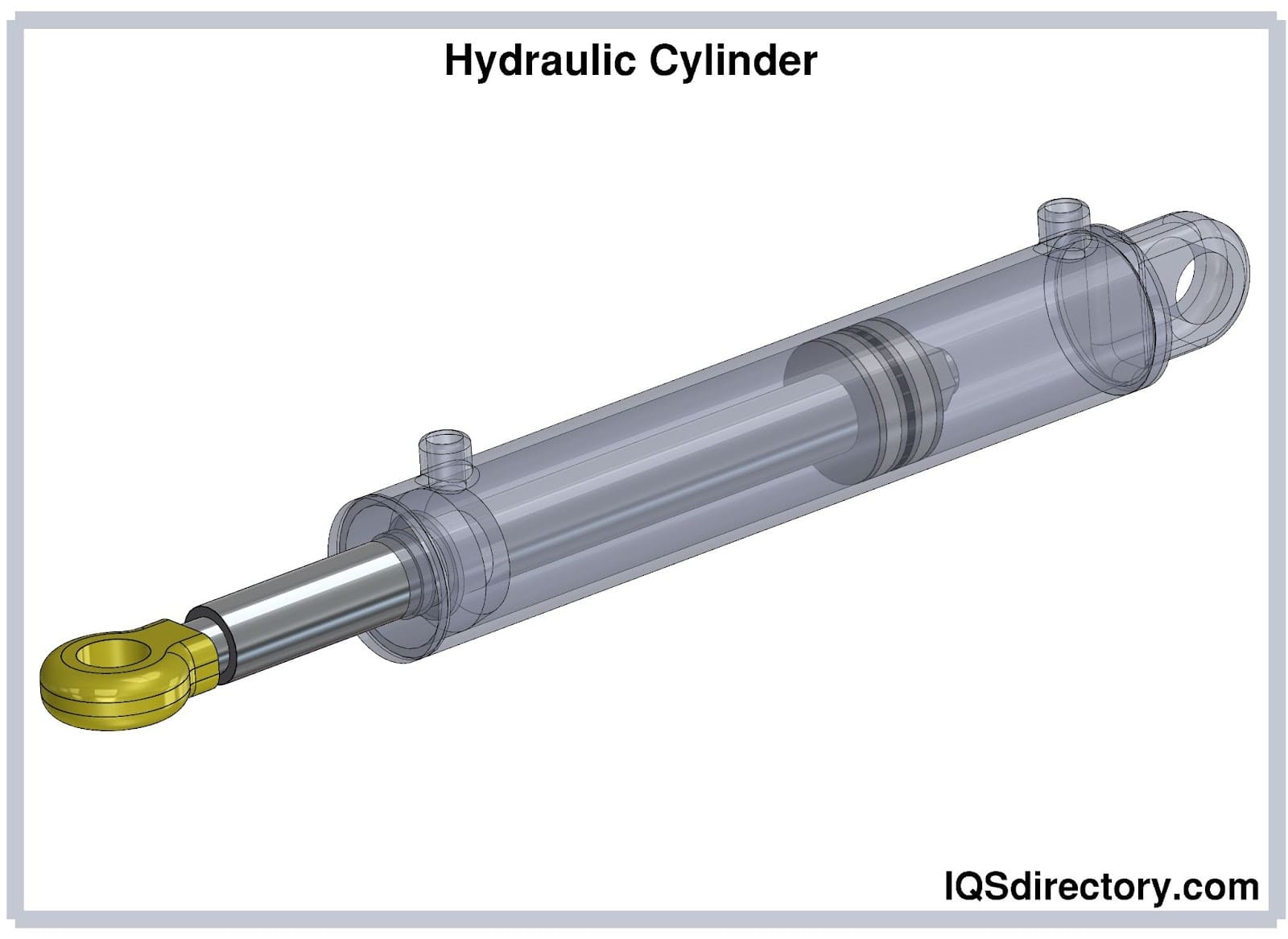
- Limited force compared to hydraulics: Air cylinders generally produce lower forces than similarly sized hydraulic actuators, making them less suitable for extremely heavy-duty tasks.
Careful system design, regular maintenance, and proper component selection can mitigate many of these drawbacks, ensuring reliable and safe operation.
Choosing the Best Compressed Air Cylinder Supplier or Manufacturer
When sourcing compressed air cylinders for your automation or industrial project, selecting a reputable manufacturer or supplier is crucial. To ensure you achieve the best results, follow these steps:
- Compare multiple suppliers: Evaluate at least 4 or 5 companies from our comprehensive list of compressed air cylinder manufacturers to gauge product quality, customization options, and industry reputation.
- Assess expertise and capabilities: Each manufacturer profile highlights their experience, certifications (such as ISO or CE), and technological offerings (custom cylinder design, rapid prototyping, etc.).
- Review application support: Top suppliers provide detailed technical data, CAD models, and engineering support to help you specify the right cylinder for your needs.
- Use direct communication: Contact manufacturers using built-in forms to request information, technical guidance, or a personalized quote for your application.
- Evaluate digital resources: Take advantage of our proprietary website previewer to explore each company’s specialties, product catalog, and past projects.
- Request multiple quotes: Use our simple RFQ (request for quote) form to contact several companies at once, streamlining your procurement process and ensuring competitive pricing.
Ready to find the right pneumatic cylinder supplier? Contact manufacturers and request a quote to start your sourcing journey.
Frequently Asked Questions About Compressed Air Cylinders
- How do I determine the correct size of pneumatic cylinder for my application? Begin by calculating the required force (using the formula: Force = Pressure x Area), then consider stroke length, mounting style, and cycle rate. Consult manufacturer sizing guides for optimal results.
- What maintenance do compressed air cylinders require? Regularly check for leaks, lubricate seals if required, inspect mounting hardware, and ensure proper alignment to extend service life and maintain performance.
- Are pneumatic cylinders suitable for cleanroom or food-grade environments? Yes, many manufacturers offer cylinders constructed from stainless steel or with special seals for contamination-sensitive applications.
- Can I retrofit sensors or switches to my existing cylinders? Many modern cylinders are designed with slots or mounts for reed switches, proximity sensors, or position feedback, enabling easy integration into automated systems.
- Which is better: pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders? Pneumatic cylinders are lighter, faster, and cleaner, making them ideal for automation, packaging, and light to moderate force applications. Hydraulic cylinders deliver higher force and are preferred for heavy-duty, high-load environments.
Have more technical or purchasing questions? Contact our experts for personalized guidance on pneumatic actuator selection, integration, and maintenance.
Conclusion: Empower Your Automation with Compressed Air Cylinders
Compressed air cylinders are the driving force behind efficient, flexible, and cost-effective motion in today’s automated world. Their unmatched versatility, safety, and ease of integration make them the preferred solution for countless industrial, commercial, and OEM applications. By understanding the different cylinder types, their advantages and limitations, and the key factors in selection and sourcing, you can unlock maximum productivity and reliability in your systems.
Whether you are upgrading an existing production line, designing a new automated process, or simply seeking to improve efficiency, choosing the right pneumatic cylinder is a decision that pays dividends for years to come. Explore our extensive resources, compare top manufacturers, and request expert support to find the ideal air cylinder solution for your operation.


 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services