Bimba Manufacturing produces air cylinders, stainless steel air cylinders, rodless cylinders and a variety of other cylinders. We provide custom-designed air cylinders, quick delivery and a company-wide commitment to quality. Contact us for your cylinder needs today!
A world-class manufacturer of pneumatic, electro-mechanical & control components & systems, Festo has more than 75 years of experience in providing customer-driven automation solutions & service. Our vast selection of air cylinders includes a range of pneumatic cylinders that offer optimized performance for every application, with products meeting demands for the pharmaceutical industry.
Falcon Industries is a machine shop and manufactures hydraulic and air cylinders to your exacting specifications. Our air cylinders are lightweight and durable. We specialize in repairable air cylinders for end dump trailers and belly (bottom) dump trucks, as well as pneumatic cylinders.

More Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturers
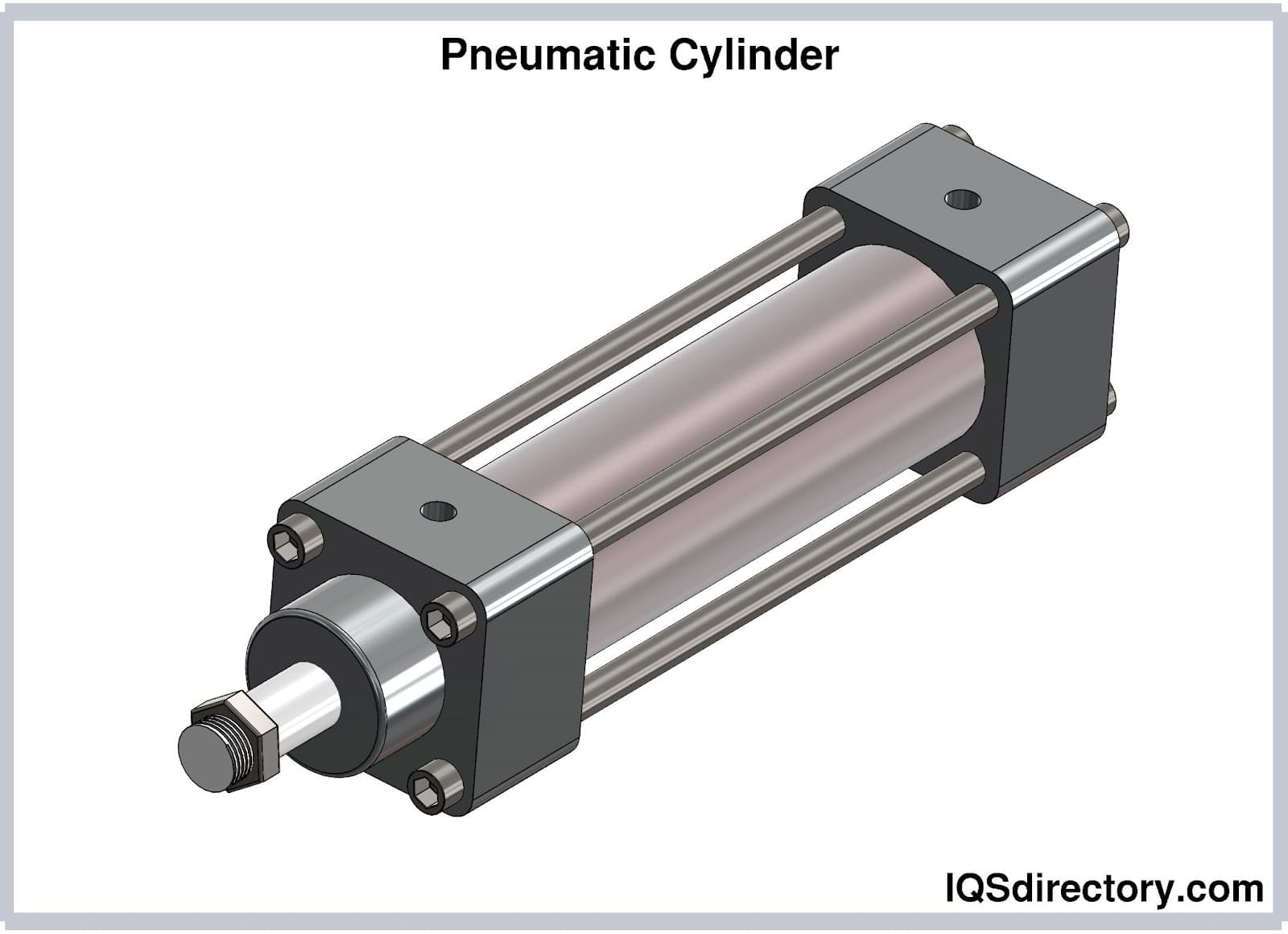
Pneumatic cylinders, also known as air cylinders, are mechanical devices engineered to use the energy derived from compressed air to generate linear motion and mechanical force. These essential components are widely used in industrial automation, manufacturing processes, robotics, and various mechanical systems. Pneumatic cylinders typically consist of three main parts: the cylinder barrel, piston, and piston rod. When compressed air enters the cylinder chamber, it increases pressure on one side of the piston, causing it to move in the desired direction. This linear force is then transmitted to the target object or load through the piston rod, enabling precise pushing, pulling, lifting, or positioning actions.
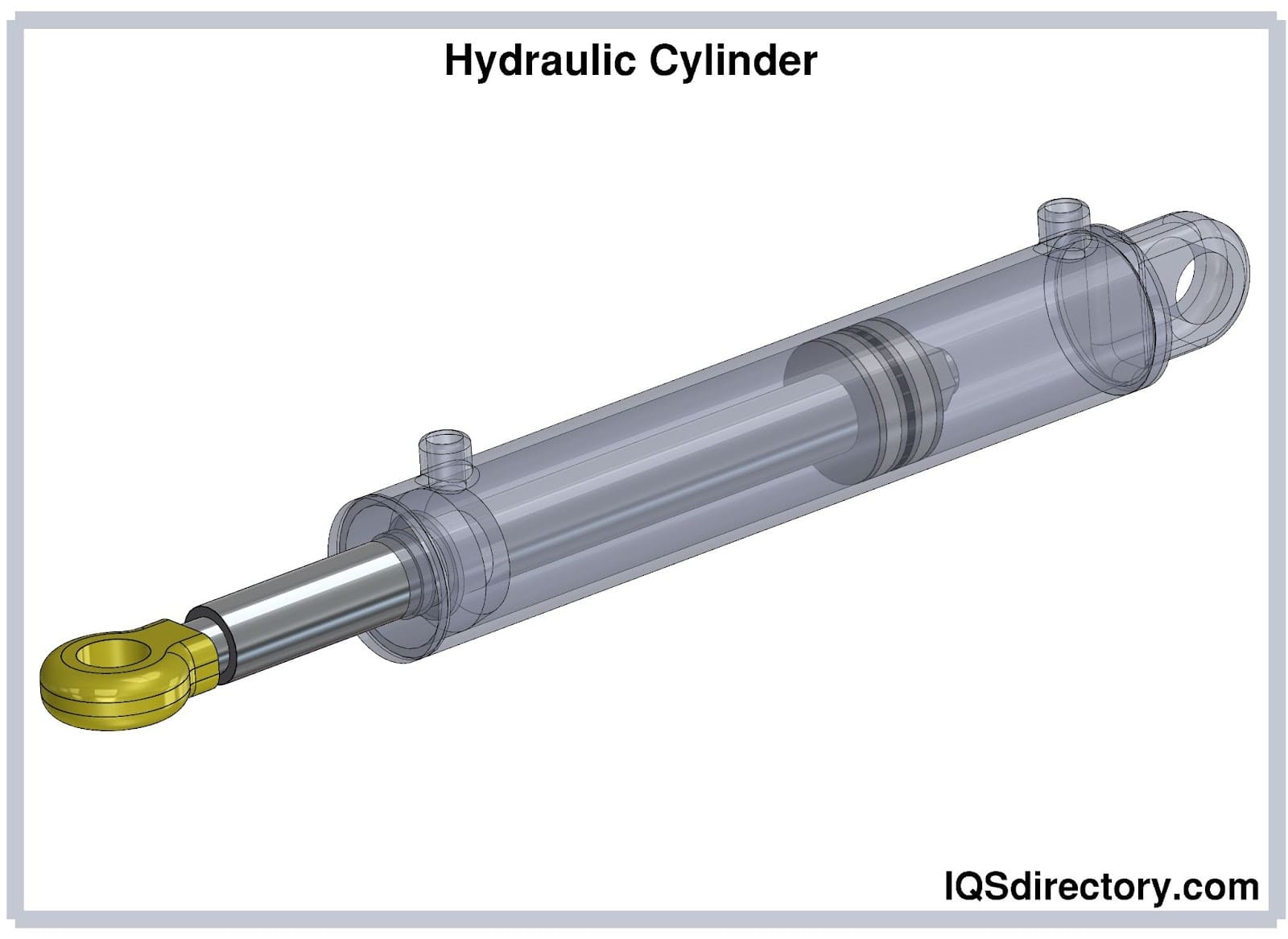
Much like hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic cylinders harness an external power source to move pistons as required. However, pneumatic actuators are often preferred for their efficiency, cleanliness, and reduced maintenance requirements. Pneumatics operate using air as the working medium, eliminating the risk of fluid leaks that can contaminate work environments or machinery. This makes pneumatic actuators ideal for industries with stringent cleanliness standards, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, packaging, and electronics manufacturing. In addition, pneumatic systems are generally quieter and require less storage space for the working fluid, contributing to a more compact and streamlined system design.

Types of Pneumatic Cylinders: Designs, Functions, and Use Cases
There are several types of pneumatic cylinders, each engineered to suit specific industrial and commercial applications. Understanding the differences between these cylinder types can help users select the optimal solution based on performance requirements, space constraints, load capacity, and operational speed.
Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders are designed to use compressed air to move the piston in both extension and retraction strokes. Air pressure is alternately supplied to either side of the piston, allowing for precise bi-directional motion. This configuration provides improved control, greater force output, and consistent speed, making double-acting cylinders suitable for heavy-duty automation, material handling, and high-cycle industrial operations.
When compressed air is supplied to one chamber and the opposite chamber is vented, the piston and rod assembly extend. Reversing the air supply retracts the piston. Notably, the extension stroke typically produces more force due to a larger effective area on the piston side, while the retraction stroke is faster because the piston rod reduces the chamber volume. Double-acting cylinders are often deployed in automated machinery, clamping applications, large valve actuation, and robotics—anywhere high force and repeatable, controlled motion are required.
- Key benefits: Bi-directional power, stable force, longer strokes, and rapid, precise motion.
- Typical applications: Packaging equipment, pick-and-place robotics, automotive assembly, industrial gates and doors, and process automation.
- Considerations: Requires more compressed air and a robust cushioning system. Higher initial cost, but supports demanding, high-speed, and high-force tasks.

Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
Single-acting pneumatic cylinders utilize compressed air to move the piston in only one direction—either extending (push-type) or retracting (pull-type). The return motion is typically powered by a built-in spring or gravity. Air enters the chamber via one port, moving the piston until it reaches its maximum stroke. Once air pressure is released or vented, the spring returns the piston to its original position.
This simple design makes single-acting cylinders more compact, lighter, and cost-effective compared to double-acting types. They are ideal for applications where force is required in only one direction, such as clamping, stamping, lifting, or ejecting components. If a system experiences a pressure loss or power failure, the spring ensures the piston returns to its default position, providing a fail-safe mechanism.
- Key advantages: Lower air consumption, compact footprint, reduced complexity, and enhanced safety in certain scenarios.
- Applications: Punching, clamping, product positioning, light-load ejection, door or gate actuation, and safety interlocks.
- Limitations: Shorter stroke length (limited by spring size), reduced force output compared to double-acting cylinders, and possible spring wear over time.

Rodless Pneumatic Cylinders
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are innovative devices that deliver linear motion over long distances while minimizing overall system length. Instead of an external piston rod, these cylinders use an internal piston connected to an external carriage or slide, which moves along the cylinder body when air pressure is applied. This configuration is highly advantageous in applications with limited space or where the stroke length must be equal to or greater than the cylinder body itself.
Rodless cylinders are available in several designs, including magnetic coupling, mechanical linkage, and band types. They enable high-speed actuation, precise positioning, and synchronized multi-axis motion. End-of-stroke cushioning is often required to absorb the momentum and protect the cylinder from impact damage.
- Benefits: Space-saving design, long stroke capabilities, smooth motion, and minimal external components.
- Typical uses: Material transfer in conveyor systems, packaging machinery, automated assembly lines, and large-format printing equipment.
- Decision factors: Load weight, required stroke length, mounting options, and environmental considerations such as dust or moisture.
Cushioned Pneumatic Cylinders
Cushioned pneumatic cylinders incorporate built-in end-of-stroke cushioning mechanisms—such as adjustable air cushions or elastomer bumpers—to absorb kinetic energy and reduce impact forces. This feature prolongs cylinder life and minimizes noise, making these cylinders ideal for high-speed automation and applications with frequent start-stop motion.
- Common applications: Automated packaging, material handling, high-speed robotics, and precision assembly operations.
- Why choose cushioned models? Enhanced durability, quieter performance, and reduced wear on cylinder seals and end caps.
Compact and Miniature Pneumatic Cylinders
For applications with strict space constraints or where lighter actuation is required, compact pneumatic cylinders and miniature air cylinders offer powerful solutions. These units provide high force output relative to their size and are commonly used in electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing, and laboratory automation.
- When to use compact cylinders? Ideal for integration into tight machinery spaces or lightweight end-of-arm tooling.
- Miniature cylinder benefits: Precision actuation, low weight, and reliable performance in delicate operations.
Pneumatic Cylinder Applications: Industry Use Cases and Buyer Intent
Pneumatic air cylinders are integral to a wide array of industries, providing reliable and efficient actuation solutions for countless processes. Below are some of the most prevalent applications and use cases:
- Industrial Automation: Pneumatic cylinders are core components in automated assembly lines, conveyors, pick-and-place robots, and packaging systems. Their fast response time and repeatable motion drive productivity in factories worldwide.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Air cylinders are employed for car and truck suspension systems, automated welding, clamping, material transfer, and even robotic painting. Their durability and precision make them indispensable in vehicle assembly plants.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Pneumatic actuators excel in sanitary environments, where contamination from hydraulic fluids must be avoided. Applications include bottling, sorting, filling, capping, and packaging.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Device Production: Because pneumatic cylinders operate cleanly and are easy to sterilize, they are used in pill sorting, packaging, and device assembly systems.
- Material Handling: Pneumatic cylinders power lifts, hoists, and conveyor diverters, streamlining warehouse logistics and order fulfillment.
- Printing and Paper Industries: Air cylinders control presses, cutters, stackers, and feeders, ensuring precise paper handling and print registration.
- Textile and Electronics Manufacturing: Used for tensioning, cutting, pressing, and component placement where delicate, rapid, and contamination-free operation is necessary.
- Mining and Heavy Equipment: Pneumatic actuators are suitable for environments where hydraulic fluid leaks could pose safety hazards or environmental risks.
Wondering how to select the best pneumatic cylinder for your application? Ask yourself:
- What load force and stroke length are required?
- Is space a limiting factor in your machine or system design?
- Will the cylinder operate in a cleanroom, food-grade, or hazardous environment?
- How important are speed, precision, and repeatability?
- What are your maintenance, budget, and lifecycle expectations?
Advantages of Pneumatic Cylinders Over Hydraulic and Electric Actuators
Why do so many engineers, designers, and operations managers choose pneumatic cylinders over hydraulic or electric actuators? Here are the key advantages:
- Cleaner operation: No risk of fluid leaks contaminating products or the environment, making them suitable for sensitive and sanitary applications.
- Lower maintenance: Fewer moving parts and simplified construction reduce the need for frequent servicing and minimize downtime.
- Energy efficiency: Pneumatic systems can be more energy-efficient for intermittent, high-speed actuation tasks.
- Quieter performance: Air-powered cylinders typically generate less noise than hydraulic systems, supporting a safer and more pleasant workplace.
- Cost-effectiveness: Lower upfront and ongoing maintenance costs, with a broad selection of standard sizes and configurations available off the shelf.
- Safety: Air is non-flammable and non-toxic, reducing fire and health hazards compared to hydraulic fluids.
- Fast response: Rapid actuation supports high-cycle production and quick machine adjustments.
Key Selection Criteria for Pneumatic Cylinders
When researching and comparing pneumatic cylinders for your project, consider these critical factors to ensure you choose the best actuator for your requirements:
- Bore size and stroke length: Determines the force output and range of motion.
- Mounting style: Includes basic, flange, clevis, trunnion, and foot mounts to suit different installation needs.
- Operating environment: Consider exposure to dust, moisture, temperature extremes, or corrosive materials. Stainless steel or specialized seals may be necessary.
- Cylinder type: Single-acting, double-acting, rodless, tandem, or compact types should be matched to the application.
- Cushioning and speed control: Essential for high-speed or heavy-load applications to prevent damage and ensure smooth operation.
- Port size and thread type: Must be compatible with your air supply and system fittings.
- Compliance and certifications: Verify FDA, ISO, or other industry standards if required for your industry.
Need help sizing or configuring your air cylinder? Try searching for:
- “How do I calculate pneumatic cylinder force and stroke?”
- “What mounting options are best for my application?”
- “How to select pneumatic cylinder seals for harsh environments?”
- “Standards for food-grade pneumatic cylinders”
Choosing the Right Pneumatic Cylinder Supplier: Tips for Buyers and Engineers
To ensure optimal results when sourcing Pneumatic Cylinders from a reputable Pneumatic Cylinder Supplier, it’s essential to follow a systematic evaluation and comparison process. Here’s how to make an informed purchasing decision:
- Shortlist multiple manufacturers: Compare at least four suppliers using a comprehensive Pneumatic Cylinder directory. Each supplier’s business profile provides detailed insights into their product range, expertise, and capabilities.
- Assess specialization and experience: Review the manufacturer’s website and online presence using available tools or website previewers. Look for companies with proven experience in your industry or with your required cylinder type (e.g., double-acting, rodless, stainless steel, compact, or ISO-standard cylinders).
- Request customized quotes: Use simple RFQ (Request for Quote) forms to reach out directly to multiple suppliers. Share your technical requirements—such as cylinder type, bore and stroke size, mounting, and operating conditions—to receive tailored proposals.
- Evaluate value-added services: Consider suppliers offering engineering support, rapid prototyping, 3D CAD models, quick turnaround times, and after-sales technical assistance.
- Check certifications and quality standards: Ensure the manufacturer complies with relevant standards such as ISO 15552, ISO 6431, or industry-specific requirements for food, pharma, or cleanroom applications.
- Review testimonials and case studies: Look for customer feedback, references, or application case studies that demonstrate successful project outcomes and reliable partnership history.
By following these steps, you can confidently select a pneumatic cylinder supplier who meets your performance, budget, and delivery requirements. Whether you need standard air cylinders for automation or custom solutions for specialized machinery, choosing the right manufacturer is crucial for long-term system reliability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pneumatic Cylinders
Q: What are the main maintenance requirements for pneumatic cylinders?
A: Routine inspections of seals, lubrication of moving parts, checking for air leaks, and cleaning of ports and surfaces are typically sufficient. Pneumatic cylinders are valued for their low-maintenance operation compared to hydraulics.
Q: How do I extend the service life of my pneumatic cylinder?
A: Use clean, dry compressed air, install appropriate filters and lubricators, avoid side loads, and ensure proper alignment and mounting. Consider choosing cylinders with corrosion-resistant finishes or materials for harsh environments.
Q: Can pneumatic cylinders be used in hazardous environments?
A: Yes, but select models with appropriate certifications and materials, such as stainless steel or ATEX-rated components for explosive atmospheres. Always consult the supplier for application-specific guidelines.
Q: How do pneumatic cylinders compare to electric actuators?
A: Pneumatic cylinders are generally faster, simpler, and more cost-effective for repetitive, high-speed tasks, while electric actuators offer superior positional control and programmability for complex motion profiles.
Explore and Compare Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturers
Ready to take the next step? Browse leading pneumatic cylinder manufacturers and suppliers to discover a wide selection of standard and custom air cylinders tailored to your industry needs. Use our advanced search tools and directory to:
- Research product specifications, datasheets, and CAD models
- Request detailed quotes and lead time information
- Contact technical support for design or troubleshooting advice
- Compare certifications, materials, and customization options
Whether you’re upgrading existing equipment, building a new automation line, or designing specialized machinery, partnering with the right pneumatic cylinder supplier is essential for project success. Start your search today and power your operations with the efficiency, precision, and reliability of modern pneumatic actuator technology.


 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services